

A lower debt to capital ratio usually means that a company is a safer investment, whereas a higher ratio means it’s a riskier bet. Another popular calculation that potential investors or lenders might perform while figuring out the health of your business is the debt to capital ratio. Although average debt ratios vary widely by industry, if you have a debt ratio of 40% or lower, you’re probably in the clear. If you have a debt ratio of 60% or higher, investors and lenders might see that as a sign that your business has too much debt. Current liabilities are debts that you have to pay back within the next 12 months.
Examples of Liabilities
- Liabilities are an effective way of getting money and is preferred over raising capital using equity.
- A modification is treated as a separate lease if it adds a new asset and increases the lease scope by commensurate consideration.
- Unlike assets, which you own, and expenses, which generate revenue, liabilities are anything your business owes that has not yet been paid in cash.
- You can calculate your total liabilities by adding your short-term and long-term debts.
- Modern tools and technologies are revolutionising liability management, making it easier than ever for businesses to streamline their processes and make data-driven decisions.
- These are the periodic payments made by a lessee (the business) to a lessor (property owner) for the right to use an asset, such as property, plant or equipment.
Non-Current liabilities are the obligations of a company that are supposed to be paid or settled on liability accounts a long-term basis, generally more than a year. Shopping for small business accounting software can be painful and confusing. To make your search easier, we’ve narrowed it down to these twelve picks. In most cases, lenders and investors will use this ratio to compare your company to another company.
What is a Liability, Examples, Types, its Placement, etc?
- As businesses continuously engage in various operations, their liability position can change frequently.
- Liabilities can further be classified into several distinct types.
- Not sure where to start or which accounting service fits your needs?
- By analyzing the types, amounts, and trends of a company’s liabilities, it is possible to gauge its financial position, stability, and risk exposure.
- By understanding what liabilities are, how they work, and their potential impact, you can make informed decisions that safeguard your business’s future.
- Proper management of these liabilities is essential to ensure smooth business operations and long-term financial health.
In simple terms, business liabilities refer to the financial and legal obligations a business owes to others. Amortization of lease liabilities involves the gradual reduction of the liability over the lease term, reflecting principal and interest payments. This is calculated using the effective interest method, impacting financial indicators such as interest coverage ratios and operating cash flows. Portions of long-term liabilities can be listed as current liabilities on the balance sheet. Most often the portion of the long-term liability that will become due in the next year is listed as a current liability because it will have to be paid back in the next 12 months. Your total liabilities plus total equity must be the same number as your total assets.
Debt Ratio: Definition, Formula (+ Free Calculator)


Liabilities in accounting are crucial for understanding a company’s financial position. They represent obligations or debts that a business owes to other parties, such as suppliers, lenders, and employees. Liabilities can take various forms, like loans, mortgages, or accounts payable, and play a significant role in determining a company’s financial health and risk. They are vital components of a balance sheet, which is one of the primary financial statements used by stakeholders to assess a company’s performance and sustainability.
- In financial accounting, a liability is a quantity of value that a financial entity owes.
- Let’s define each element in turn and then discuss how the elements relate to each other.
- Under U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), some contingent losses may be reported on the balance sheet and income statement, while others are only disclosed in the footnotes.
- Let’s look at a historical example using AT&T’s (T) 2020 balance sheet.
- There are many different types of liabilities including accounts payable, payroll taxes payable, and bank notes.
- To calculate total liabilities, simply add up all of the liabilities the business has.
Sandra’s areas of focus include advising real estate agents, brokers, and investors. She supports small businesses in growing to their first six figures and beyond. Alongside her accounting practice, Sandra is a Money and Life Coach for women in business. Other balance sheets are presented using the report-form method, which is the most common method of balance sheet presentation. Learn how automated accounting software Partnership Accounting simplifies financial management with efficiency.


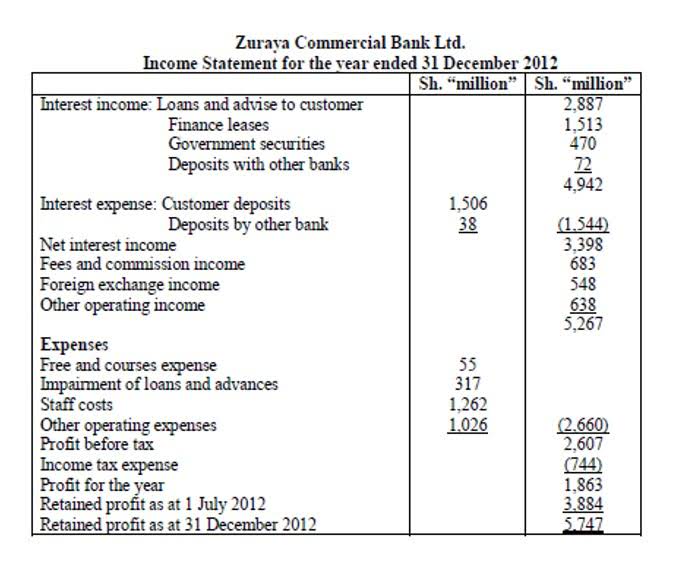

In conclusion, liabilities play a crucial role in business operations, as they represent the financial obligations a company has to its employees, suppliers, lenders, and other stakeholders. Proper management of these liabilities is essential to ensure smooth business operations and long-term financial health. Liabilities are carried at cost, not market value, like most assets. They can be listed in order of preference under generally accepted accounting principle (GAAP) rules as long as they’re categorized.
Understanding Tenant Compensation for Inconvenience in Queensland: A Complete Guide


Different types of liabilities are listed under each category, in order from shortest to longest term. Accounts payable would be a line item under current liabilities while a mortgage payable would be listed under long-term liabilities. Pension obligations are crucial to understanding a company’s commitment to its employees and the potential strain on future resources. Accurately accounting for pension obligations can be complex and may require actuarial valuations to determine the present value of future obligations. An expense is the cost of operations that a company incurs to generate revenue.
- Just as you wouldn’t want to take on a mortgage that you couldn’t easily afford, it’s important to be strategic and selective about the debt you assume as a business owner.
- Get free guides, articles, tools and calculators to help you navigate the financial side of your business with ease.
- These are obligations owed to other entities, which must be fulfilled in the future, usually by transferring assets or providing services.
- The carrying amount may be adjusted for remeasurements of the lease liability or impairment losses.
- Portions of long-term liabilities can be listed as current liabilities on the balance sheet.
- And if you have more debt, then you’re going to have higher liabilities.
Contingent liabilities
Liabilities can further be classified into several distinct types. Sign retained earnings balance sheet up to receive more well-researched small business articles and topics in your inbox, personalized for you. We’ll break down everything you need to know about what liabilities mean in the world of corporate finance below. Maybe it’s because you bought them a drink or did a favor for them.